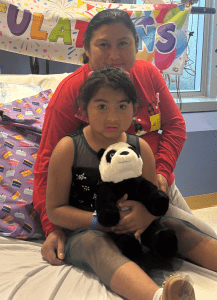
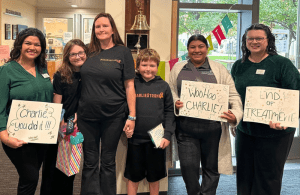Katie age 16 Diagnosis:
Katie age 16 Diagnosis:
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia– Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects the body’s white blood cells (WBCs). Normally, WBCs help fight infection and protect the body against disease. But in leukemia, WBCs turn cancerous and multiply when they shouldn’t, resulting in too many abnormal WBCs, which then interfere with organ function.
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia– CML is caused by a chromosomal problem. The 23 pairs of chromosomes in the body each contain segments of DNA called genes. Genes are essentially the body’s blueprints.
CML occurs when a piece of chromosome 22 breaks off and switches places with a piece of chromosome 9. (This piece, containing parts of both chromosome 9 and chromosome 22, is known as the Philadelphia chromosome.) The combination results in the cancer gene known as BCR-ABL. This is the gene that instructs the body to make too many mature WBCs